Source: http://intro2atria2009.blogspot.com/2009/12/clase-28.html; Accessed 2-19-0=2010.
FUNCIÓN DE LA FUNCIÓN
1. Identificación de la función.
2. ¿Por qué la función es improbable sin estructura?
3. Estructura que neutralice la improbabilidad.
4. la estructura hace probable, y no necesario, el cumplimiento de la función.
Sometimes Reach Reading™ requires a researcher to look at articles in other languages than he or she knows. Hmmm! That won't stop someone who wants to know something, He or she will, "Reach!"
Then, a translation tool, for example, http://webdev.quickfound.net/language_translation_tools.html might be useful and we can look at more of the web page, too:
Class 28
9 noviembre 2009
November 9, 2009
Por Sebastián Jara L.
By Sebastian Jara L.
Concepto Jurídico no es Estructural.
Legal Concept is not structural.
Tiene una explicación funcional (en definitiva) y nominal.
It has a functional explanation (ultimately) and nominal.
Esto se hace evidente al analizar al Derecho Penal.
This becomes evident when analyzing the Criminal Law.
Ergo, la pena, y al diferenciarla del tributo.
Ergo, grief, and differentiate the tax.
El tributo se diferencia de la multa en su función.
The tribute to the fine difference in function.
La pena tiene carácter de reproche.
The penalty is a matter of reproach.
Según Moore la pena infringe reproche por conductas que van en contra de principios morales verdaderos.
According to Moore's sentence for conduct that violates reproach go against moral principles true.....
FUNCIÓN DE LA FUNCIÓN
ROLE OF THE ROLE
1. Identificación de la función.
Identification of the function.
2. ¿Por qué la función es improbable sin estructura?
Why the function is unlikely without structure?
3. Estructura que neutralice la improbabilidad.
Structure to neutralize the improbability.
4. la estructura hace probable, y no necesario, el cumplimiento de la función.
structure makes it likely, and not to the fulfillment of the function.
FUNCIÓN DE LA FUNCIÓN دور دور
. 1 Identificación de la función. تحديد وظيفة.
. 2 ¿Por qué la función es improbable sin estructura? لماذا وظيفة من غير المرجح بدون الهيكل؟
. 3 Estructura que neutralice la improbabilidad. هيكل لتحييد الاحتمال.
. 4la estructura hace probable, y no necesario, el cumplimiento de la función. هيكل يجعل من المحتمل ، وعدم وفاء للمهمة.
ROL VAN DIE ROL
1. Identificación de la función. Identifikasie van die funksie.
2. ¿Por qué la función es improbable sin estructura?
Waarom die funksie wat dit onwaarskynlik is sonder struktuur?
3. Estructura que neutralice la improbabilidad.
Struktuur te neutraliseer die onwaarschijnlijk.
4. la estructura hace probable, y no necesario, el cumplimiento de la función.
struktuur maak dit waarskynlik is, en nie aan die vervulling van die funksie.
If we see then that the article is not what we wanted, though it is an interesting article on legal concept of function/role, then we can continue our search on functions of a mathematical nature.
How about this one?
http://functions.wolfram.com/
General
The arithmetic-geometric mean appeared in the works of J. Landen (1771, 1775) and J.‐L. Lagrange (1784-1785) who defined it through the following quite‐natural limit procedure:

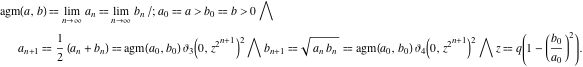 C. F. Gauss (1791–1799, 1800, 1876) continued to research this limit and in 1800 derived its representation through the hypergeometric function
C. F. Gauss (1791–1799, 1800, 1876) continued to research this limit and in 1800 derived its representation through the hypergeometric function.
If you are like many readers, you say, "Whoa!" as soon as you reach the equations. Slow down. Don't panic. In fact, perhaps, "whoa," is the right word. Take your time.
Compare this reading to a video game. It wouldn't be fun if you knew where all the treasures are. The fun is in the challenge. Before you get into decoding the equations and math jargon, check if the article is on what you want to learn, Then, slow down and have fun with it. You'll soon come up to speed.
Try another source:
In mathematics, the arithmetic-geometric mean (AGM) of two positive real numbers x and y is defined as follows:Does this second source help you understand better?
First compute the arithmetic mean of x and y and call it a1. Next compute the geometric mean of x and y and call it g1; this is the square root of the product xy:
Then iterate this operation with a1 taking the place of x and g1 taking the place of y. In this way, two sequences (an) and (gn) are defined:
These two sequences converge to the same number, which is the arithmetic-geometric mean of x and y; it is denoted by M(x, y), or sometimes by agm(x, y).
This can be used for algorithmic purposes as in the AGM method.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arithmetic-geometric_mean; Accessed 2-19-2010.
Sources:
http://intro2atria2009.blogspot.com/2009/12/clase-28.html; Accessed 2-19-2010.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arithmetic-geometric_mean.
More tools:
http://translate.google.com/translate_buttons
(c)2010 J S Shipman













1 comment:
From an anonymous reader:
感謝你的分享 要繼續發表好文章喔
Thank you for sharing to continue to publish a good article 喔
Post a Comment